GWLs and baseline periods
It is important to note that GWLs are expressed as changes (or anomalies) calculated with respect to a baseline reference period. While the Paris Agreement2 refers to the pre-industrial period and IPCC uses specific definitions of (near) pre-industrial periods, most commonly 1850-1900, different baseline periods may be used to define GWLs. For example, the Climate Resilient Buildings and Core Public Infrastructure Report (CRBCPI)3, which provides future building design values, uses 1986-2016 as its baseline. As such, care needs to be taken when comparing projections based on GWLs to ensure that baselines are understood.
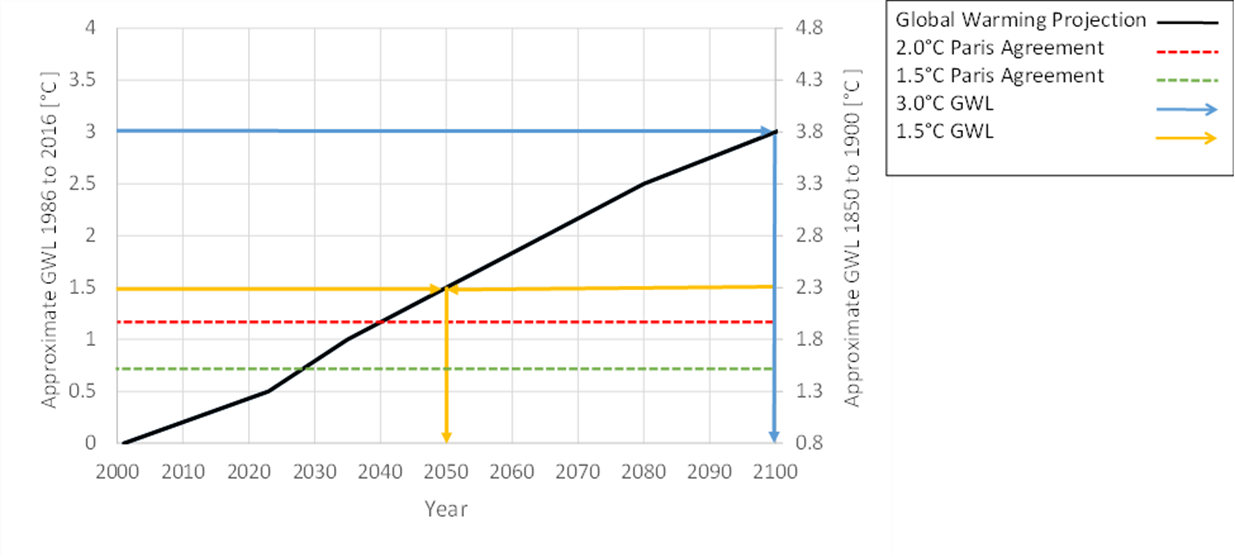
It is possible, however, to reconcile differences in baselines to standardize the definition of GWLs. For example, Figure 1 illustrates the timing of GWLs using two different baseline periods: the IPCC pre-industrial period (1850-1900; right axis) and the 1986-2016 baseline (left axis) used by CRBCPI. About 0.8°C of global warming has occurred between the IPCC and CRBCPI baselines.
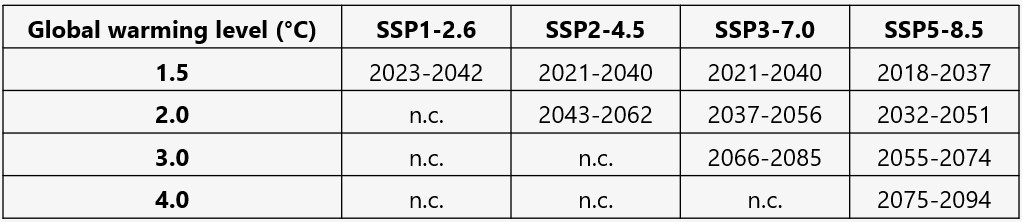
Noting that the Paris Agreement target is to limit global warming to “well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels”, in this example we compare 1.5°C and 2°C above 1850-1900 with the corresponding GWLs using the CRBCPI baseline period. The 2°C GWL above the 1850-1900 level corresponds to about 1.2°C of warming if using the 1986-2016 baseline. The 1.2°C of warming is projected to occur around 2040. Similarly, the more stringent 1.5°C target corresponds to a GWL of about 0.7°C using the CRBCPI baseline of 1986-2016 and is projected to occur in the mid-2020s.
The CRBCPI report and the Pacific Climate Impacts Consortium’s Design Value Explorer (DVE) tool provide information about future design values for a range of GWLs to supplement the information in the National Building Code of Canada. The Future Building Design Value summaries available on ClimateData.ca provide information for two GWLs, 1.5°C and 3.0°C, relevant for the design of short- to medium-term design service life components (10 to 30 years) and medium- to long-term design service life components (50+ years), respectively. These GWLs are relative to the 1986-2016 baseline and correspond to GWLs of 2.3°C and 3.8°C using the pre-industrial baseline.
Another baseline period that you may encounter is 1971-2000. About 0.5°C of global warming has occurred between the IPCC’s pre-industrial baseline reference period of 1850-1900 and 1971-2000. This means that a GWL of 2°C relative to 1971-2000 is roughly equivalent to a GWL of 2.5°C from the pre-industrial 1850-1900 baseline. Finally, while most of the time a GWL from pre-industrial means 1850-1900, there are different definitions of “pre-industrial”, so it is always important to check the actual time period that is being used to define the baseline.