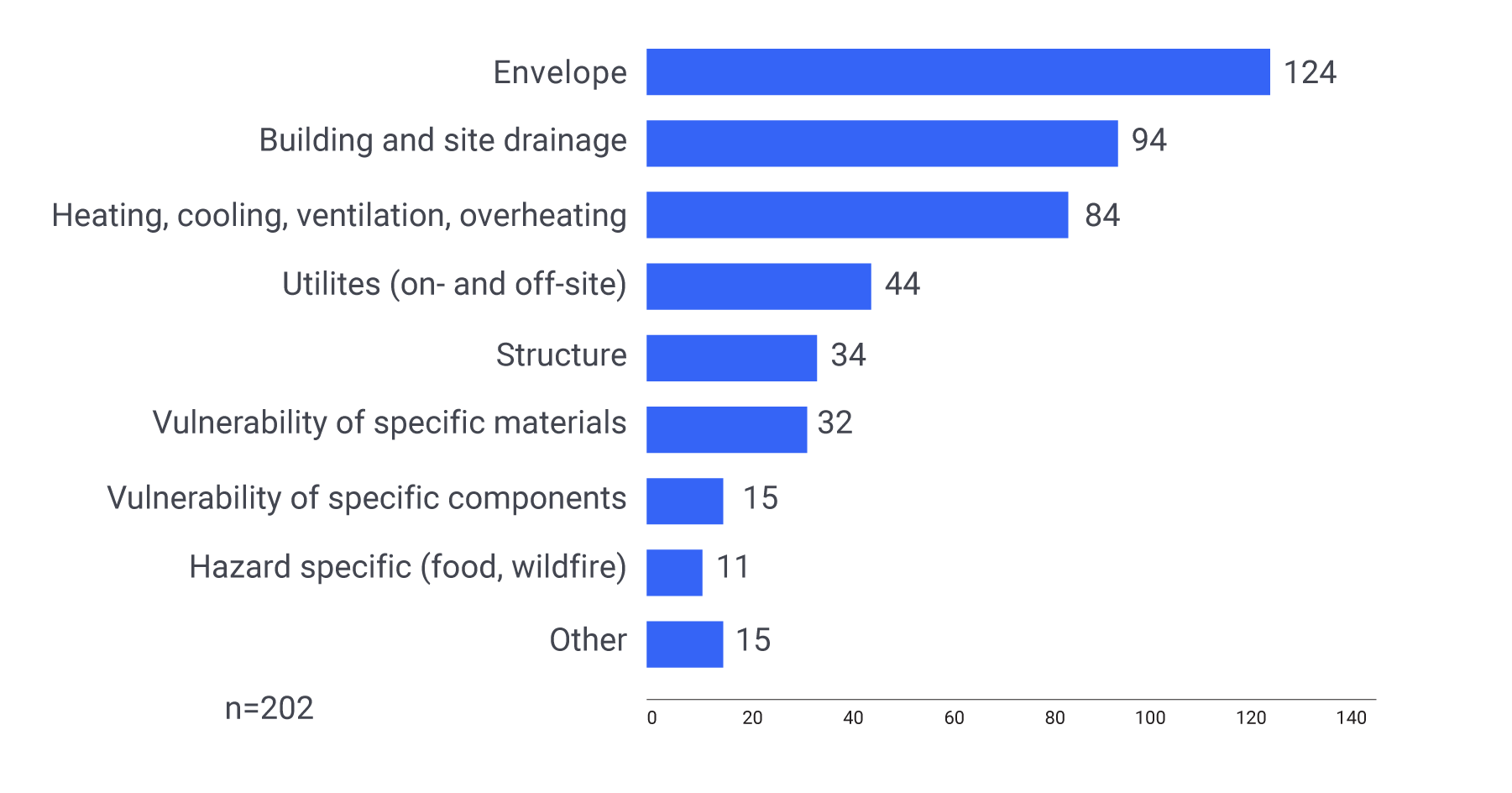
A 2020 CRBCPI report is Canada’s most detailed foray yet into providing building-specific climate change metrics. These data are being considered for adoption in the 2025 National Building Code, and are powering tools like the new climate resilience for low slope membrane roofing systems application.
Federal funding for climate-resilient buildings supports the application of new climate-aware standards, data, and codes to real world building design and retrofit. Via the federal Climate Lens and related initiatives, Infrastructure Canada is working to ensure that new major infrastructure projects initiated under funding opportunities like the Disaster Mitigation and Adaptation Fund and Green and Inclusive Community Buildings program include robust assessments of present and future climate risks, informed by national networks of communities of practice such as the Infrastructure and Buildings Working Group under Canada’s Adaptation Platform.
Provinces and territories are showing leadership in the area of climate resilient building planning and design. Examples include Ontario, which in 2016 tasked its Minister of Municipal Affairs with “…a review of the Building Code to support low-carbon standards for new buildings and to ensure that buildings continue to be safe and accessible,” and Quebec, which stated the need to “collaborate in the development of criteria, codes, guides, and other tools necessary for adapting the built environment to climate change,” in a 2013-2020 Government Strategy for Climate Change Adaptation. Provincial and territorial bodies can set a tone for change, which can spur innovative thinking. In British Columbia, for example, BC Housing’s Mobilizing Building Adaptation and Resilience project is supporting capacity building and innovation in resilient, low-carbon building design. Quebec’s Société québecoise des infrastructure (SQI) is identifying climate risks and climate adaptation measures for its institutional building stock through the use of their new assessment framework, which may be adapted for use by other interested property owners and managers.
Municipalities are uniquely positioned to accelerate climate resilience in the buildings sector, as they integrate climate change-related provisions through zoning and planning, local construction requirements, guidelines, and programs, and also provide provincial code interpretations that target regional building vulnerabilities. In many cases, existing planning pathways and governance structures (for example, disaster response and recovery) can be effectively leveraged to enable excellent, vulnerability-motivated or ‘bottom-up’ climate adaptation actions that directly address known vulnerabilities.
Where there are gaps in provincial codes, local jurisdictions have applied other regulatory tools at their disposal to reduce building vulnerability. This allows for climate considerations to be included at a local level that are tailored to unique interactions between local buildings and local climate. Increasingly, integration of future climate information into these municipal-level building and planning efforts is occurring via municipal Climate Action Plans. At the national level, the Federation of Canadian Municipalities is an important foundation for enhancing capacity and knowledge-sharing between municipalities.